
Mammography
Mammography is the process of using low-energy X-rays to examine the human breast for diagnosis and screening. The goal of mammography is the early detection of breast cancer, typically through detection of characteristic masses or microcalcifications.
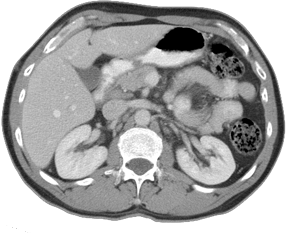
Computed
Tomography
A CT scan, or computed tomography scan, is a medical imaging procedure that uses computer-processed combinations of many X-ray measurements taken from different angles to produce cross-sectional (tomographic) images (virtual "slices") of specific areas of a scanned object, allowing the user to see inside the object without cutting.

Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to generate images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from CT and PET scans.

Vascular Interventional Imaging
Interventional radiology (IR) is a medical subspecialty that performs various minimally-invasive procedures using medical imaging guidance, such as x-ray fluoroscopy, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or ultrasound. IR performs both diagnostic and therapeutic procedures through very small incisions or body orifices. Diagnostic IR procedures are those intended to help make a diagnosis or guide further medical treatment, and include image-guided biopsy of a tumor or injection of an imaging contrast agent into a hollow structure, such as a blood vessel or a duct. By contrast, therapeutic IR procedures provide direct treatment—they include catheter-based medicine delivery, medical device placement (e.g., stents), and angioplasty of narrowed structures.